Pulmonary hypertension is a condition indicating high blood pressure in the heart-to-lung system. It affects the right side of your heart and arteries in your lung.
In healthy arteries, the blood flow is smooth. If the arteries become narrowed, blocked, or destroyed, the blood flow to the lungs gets slowed down. Therefore, your heart must work harder to pump blood to the lungs. This wears out your heart muscles, making them weak, and eventually, the heart fails.
Early detection and appropriate treatment for this condition can reduce the intensity of the symptoms and improve the quality of life.
Causes
Pulmonary hypertension can be caused by various factors related to the heart and lungs. Based on these factors, it is broadly divided into five groups.
GROUP I:
PAH (Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension)
Caused by:
1. Heritable pulmonary arterial hypertension
(Passed down in families due to changes in genes)
2. Use of illegal substances and some specific drugs
3. Congenital heart disease
(Heart diseases present since birth)
4. Idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension
(Due to any unknown cause)
5. Certain connective tissue disorders (scleroderma, lupus, etc.), HIV infection, or chronic liver diseases (cirrhosis)
GROUP II:
Pulmonary Hypertension Because Of Left-Sided Heart Disease
Caused by:
1. Mitral valve or aortic valve disease (Valves of the left side of the heart)
2. Failure of the left ventricle (lower left heart chamber)
GROUP III:
Pulmonary Hypertension due to Lung Disease
Caused by:
1. COPD
(Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease)
2. Scarring of lung tissues (pulmonary fibrosis)
3. Obstructive sleep apnoea
4. Exposure to high altitude for a long time
GROUP IV:
Pulmonary Hypertension by Chronic Blood Clots
Caused by:
1. Chronic blood clots in lungs
(Presence of pulmonary emboli)
2. Other clotting disorders
GROUP V:
Pulmonary Hypertension Caused by Other Health Problems
Caused by:
1. Kidney diseases
2. Blood disorders (thrombocythemia and polycythemia vera)
3. Inflammatory disorders such as sarcoidosis and vasculitis
4. Metabolic disorders, like glycogen storage disease
5. Tumours pressing against pulmonary arteries
Symptoms
The symptoms of pulmonary hypertension are undetectable during the initial stages of the disease. They become prominent after several months, making diagnosing the condition difficult.
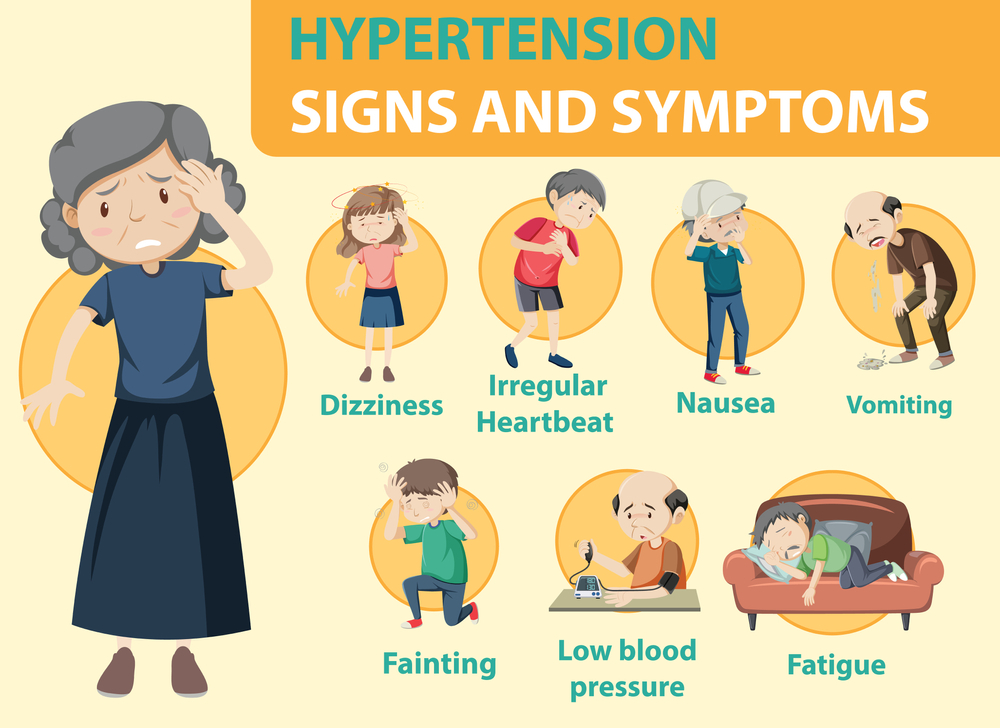
Some of the main symptoms include:
1. Shortness of breath during various types of physical activities
2. Fatigue or lack of energy
3. Dizziness may result in fainting.
4. Chest pressure
5. Chest pain
6. Rapid pulse
7. Heart palpitations
8. Bluish tint to your lips or skin
9. Swelling of your ankles or leg
10. Swelling in the abdomen during later stages of the disease
In later stages, breathing becomes difficult in resting positions also.
Risk Factors
AGE:
Age is a significant risk factor in this condition. Mostly, people between the age of 30 and 60 face a higher risk. Older patients suffering from this disease must be more cautious as they experience more complications.
FAMILY HISTORY:
If someone in the family already has pulmonary hypertension, there is a significant chance that it will be passed down to the younger generation.
OBESITY:
Excessive body weight puts the patient at higher risk.
MEDICATION:
Some medicines used for weight loss or the treatment of depression can have some adverse effects on the patient suffering from pulmonary hypertension.
DRUG ADDICTION:
Addiction to various kinds of drugs
HIGHER ALTITUDE LOCATION:
If someone lives in a high-altitude region for the long term, they may gradually develop the disease.
ASBESTOS EXPOSURE:
Prolonged exposure to asbestos particles poses a high risk of developing this disease.
Clinical Treatments
The treatment for pulmonary hypertension varies from patient to patient, depending on the patient's symptoms. The medications prescribed by the doctor are targeted at reducing your problematic symptoms, such as:
1. Vasodilators
Vasodilators are for dilating blood vessels that have become narrower. The doctor can administer these drugs orally and intravenously, or they can be inhaled through a nebulizer.
2. Calcium Channel Blockers
Calcium channel blockers for decreasing blood pressure in your lungs and the whole body. The walls of the blood vessels get relaxed due to this.
3. Warfarin
Warfarin is an anticoagulant, which means it dissolves any blood clot that may be present in your lung capillaries.
4. Oxygen Therapy
Oxygen therapy, in which pure oxygen is provided for inhalation. Your doctor may prescribe this if you are going to a higher altitude or have sleep apnea. This therapy is often needed in the later stages of the disease, even during simple physical movements.
5. Diuretics
Diuretics help the kidneys in better removal of extra fluids. Hence, your body parts will not accumulate extra fluids, and the heart can work more efficiently.
6. Guanylate cyclase stimulators
Guanylate cyclase stimulators help increase the amount of nitric acid in the body. This nitric oxide helps relax the walls of blood vessels. however, you should check with your doctor about the side effects of this drug and then proceed.
7. Endothelin receptor antagonists
Endothelin receptor antagonists can help slow the effects of endothelin, a specific peptide produced in your body (which can be found as an amino acid chain). It is responsible for blocking arteries and veins.
If none of the medicines can relieve the patient, Surgery is the option to adopt.
Atrial septostomy is the surgical procedure followed for pulmonary hypertension if all the other medicinal options cannot provide relief to the patient. In this procedure, the surgeon makes an opening between the left and right atria (the upper right and left chambers of the heart). The pressure on the right side of the heart gets relieved due to this.
Another suggested surgical procedure is the complete transplantation of the lungs
Precautions
There are some major precautions that the patient should follow to avoid making the condition more dangerous:
A. Do not take any medicines without properly discussing them with your doctor. It may not provide relief and may worsen the situation.
B. Avoid going to high-altitude regions. If you live in any region like this, consult your doctor for the necessary protocols.
C. Quit smoking as soon as possible. If not possible by yourself, ask for help. Smoking may worsen your lung conditions.
D. Regular check-up with your doctor is mandatory for a long and healthy lifestyle.
E. Avoid coffee, alcoholic drinks, or any other beverage which causes high blood pressure.
We hope this has helped you understand the various risks associated with Pulmonary Hypertension. We strongly recommend you consider prevention over cure and take utmost precautions.